What Is Cloud Storage and It’s Benefits?

Table of Contents
What is cloud storage? A third-party cloud provider owns and manages data storage and offers it via the Internet in a pay-as-you-go manner. It is indeed on-demand, only with capacities and pricing, and it saves you money by not having to acquire and manage your digital storage infrastructure. With “anytime, everywhere” data access, you get agility, global scalability, and durability.
What is meant by cloud storage?
With the basic information you have in mind, let’s figure out what cloud storage means next. Cloud storage is a cloud computing approach in which data is stored on the Internet and managed and operated by a cloud computing provider. These cloud storage providers handle capacity, security, and durability to ensure that data is available to your apps wherever in the globe.
Traditional storage methods or an API are used by applications to access cloud services. Many companies provide add-on services to aid in collecting, managing, security, and analyzing large amounts of data.
Read more about the advantages of content delivery network in the other article.
Types of cloud storage
When you learn more about what is cloud storage all about, you will also come across the need to figure out different types of cloud storage. There are three main types of cloud storage. They include file storage, object storage, and block storage. Each type of Storage comes with a set of unique use cases.
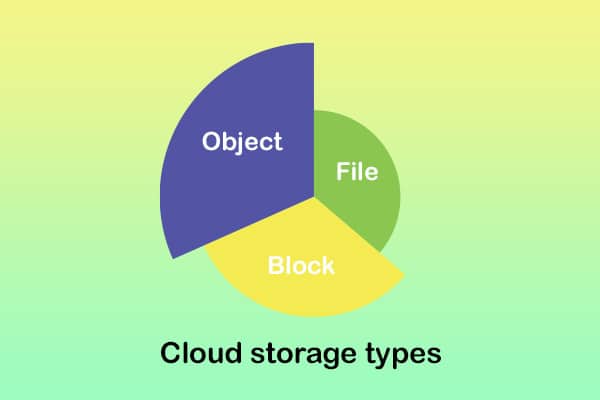
1- Object Storage
The extensive scalability and data features of datastore are often used in cloud applications. Object storage systems, such as Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3), are suitable for developing contemporary apps from the ground up that demand scalability and flexibility, as well as importing existing storage arrays for analysis, restoration, or archiving.
2- File Storage
Some programs need a file system to access shared files. A Network Attached Storage (NAS) system is often used to support this form of Storage. Major content repositories, developer tools, media stores, and user home directories are good candidates for file storage systems like Amazon Elastic File System (EFS).
3- Block Storage
Databases and ERP systems, for example, often demand dedicated, low-latency Storage for every host. Direct-attached Storage (DAS) or a Network Device is similar (SAN). Cloud storage systems based on blocks, such as Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS), are provided with each VM and provide the extremely low latency needed for high-performance applications.
If you want to buy cloud server (fastest), click here.
How does cloud storage work?

As you learn what is cloud storage definition, you should also be aware of how it works. A third-party cloud provider owns and manages storage capacity and offers it via the Internet in a pay-as-you-go manner. These cloud storage providers handleability, security, and durability to ensure that data is available to your apps wherever in the globe.
Existing storage methods or an API are used for accessing and monitoring cloud storage. Many companies provide add-on services to aid in collecting, managing, security, and analyzing large amounts of data.
What are the advantages of cloud storage?
There are numerous benefits that you can experience along with cloud storage. Let’s take a quick look at what those benefits are:

– You can reduce the overall ownership expenses
There is no need to buy hardware, provide Storage, or utilize cash for “someday” situations with cloud storage. You may add and remove space on demand, modify efficiency and durability characteristics fast, and only spend for the Storage you use. According to auditable criteria, less frequently visited data may also be automatically transferred to lesser cost tiers, resulting in cost savings.
– It provides convenience with new deployments
Infrastructure shouldn’t ever slow down game developers when they are ready to activate. Cloud storage enables IT to supply precisely the correct capacity at the right time. Instead of managing storage systems, IT can concentrate on addressing complicated application challenges.
– You can easily manage information
Centralizing Storage on the cloud provides a huge advantage for new usage cases. You may execute strong information management tasks like automatic tiering and data securing to support regulatory needs by employing online storage lifecycle management rules.
What are the disadvantages of cloud storage?
Similar to advantages, there are some disadvantages of it as well. Here are some of the most prominent disadvantages you will have to experience.
– You need to have the Internet to access it
It is necessary to access an active internet connection to access cloud storage. This can be challenging for some organizations.
– Ongoing expenses
When using the cloud, you will have to deal with ongoing costs for uploading and downloading the files.
What are cloud storage examples?

Regardless of the drawbacks, we can see how people use cloud storage for multiple purposes. Here are some of the most prominent cloud storage examples that we can see out there.
– Compliance
Data stored on the cloud may create worries about regulatory standards, mainly if the data is already in legal storage systems. Amazon Glacier Vault Lock is a cloud data compliance control that allows you to create and enforce compliance rules on individual data vaults through a lockable policy. You may use restrictions like Write Once Read Many (WORM) to prevent future changes to the data. You can achieve compliance and governance goals for your fog storage and archive systems by using audit log solutions like AWS CloudTrail.
– Recovery and backup

Backup and recovery are essential for guaranteeing data security and accessibility but maintaining up with growing capacity demands may be difficult. Cloud storage makes backup and recovery options more affordable, durable, and scalable. Embedded data management rules, such as Amazon S3 Object Life – cycle management, may move data to lower ranks depending on frequency or timing parameters. Archiving vaults can be constructed to meet legal or regulatory needs. These advantages enable massive scalability in businesses like financial products, health, and media that generate large amounts of data without long-term preservation requirements.
– Software Development and Testing
Separate, autonomous, and redundant storage systems must frequently be built up, maintained, and retired in computer development and testing environments. Aside from the time commitment, the upfront capital expenses might be substantial.
By exploiting cloud storage’s flexibility, speed, and cheap cost, some of the world’s most significant and valuable firms have produced apps at record speed. Even the most rudimentary static websites may be enhanced for a meager price. Pay-as-you-go storage options are gaining popularity among developers worldwide because they eliminate management and scaling issues.
– Data Migration
Traditional IT functional owners such as Storage, security, networking, backup, and compliance admins may worry about shifting vast quantities of data to the cloud due to cloud storage’s availability, endurance, and cost advantages. Cloud data moving services like AWS Shipping Snowball can make it easier to migrate Storage to the cloud by reducing network costs, transmission times, and security issues.
in the end we recommend read this article about which is the cheapest cloud storage?
Conclusion
Now you know what cloud migration is all about. Keep these in mind and find the best cloud available to migrate and experience these benefits.





