If you are planning to launch your first website, chances are you have already encountered two terms that seem to be used interchangeably: web hosting and domain name. At first glance, they sound like they refer to the same thing. In reality, they serve completely different purposes, and misunderstanding this difference is one of the most common reasons beginners feel overwhelmed when building a website for the first time.
The simplest way to understand the distinction is this: a domain name helps people find your website, while web hosting is what actually stores and delivers your website to visitors. You need both for a website to function properly. Having one without the other is not enough, no matter how modern your design or how good your content is.
This guide is written specifically for beginners, entrepreneurs, and small business owners who want a clear and practical explanation without unnecessary technical jargon. By the end of this article, you will understand exactly what a domain name does, what web hosting is responsible for, and how the two work together to bring a website to life.
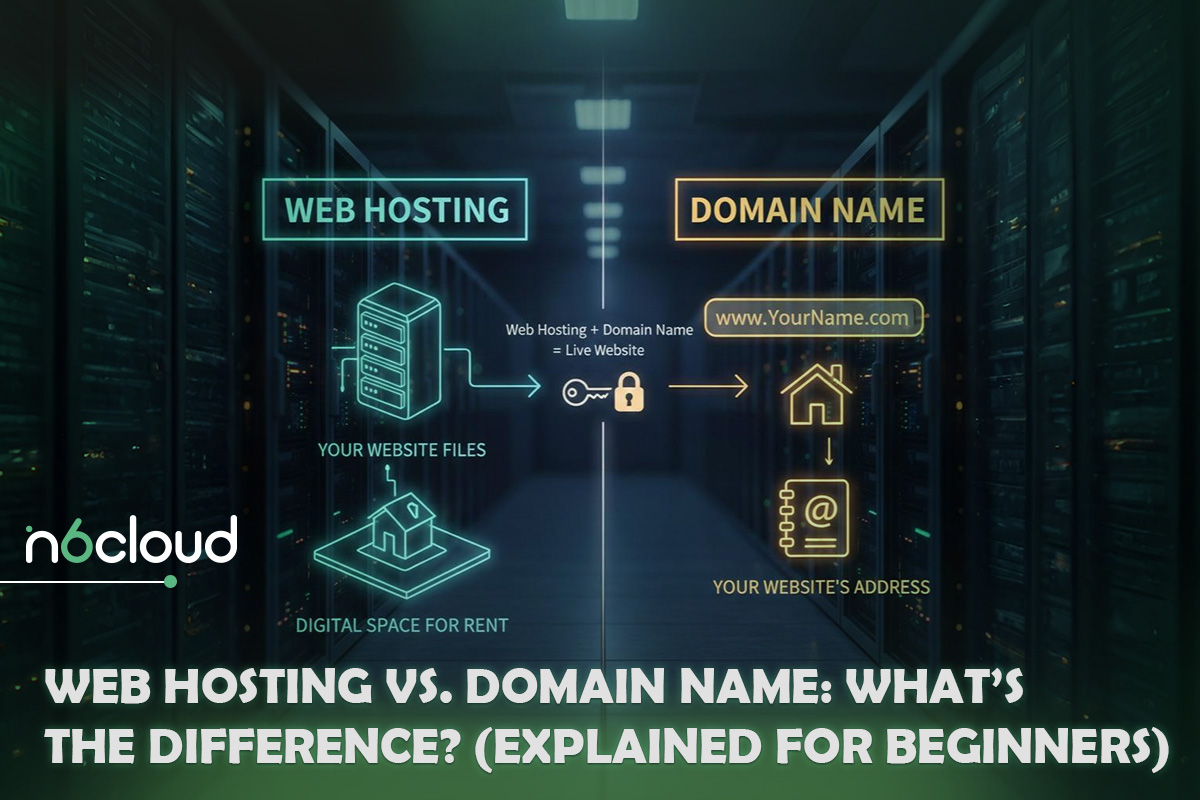
The Core Difference: Address vs. Land
One of the most effective ways to understand the relationship between a domain name and web hosting is through a real world analogy. Imagine your website as a physical house in a city. In this scenario, the domain name is the street address that people use to locate your home. It tells visitors where to go, but it does not contain anything by itself.
Web hosting, on the other hand, is the actual land and building where everything exists. It is where your furniture, documents, and personal belongings are stored. Without the building, an address points to an empty lot. Without the address, a fully built house is nearly impossible for others to find.
A functioning website requires both components working together at all times. The domain name directs visitors to the correct location, and the web hosting delivers the website content they expect to see once they arrive. Neither can replace the other, and treating them as separate but connected services is the key to making informed decisions when launching a website.
What Is a Domain Name?
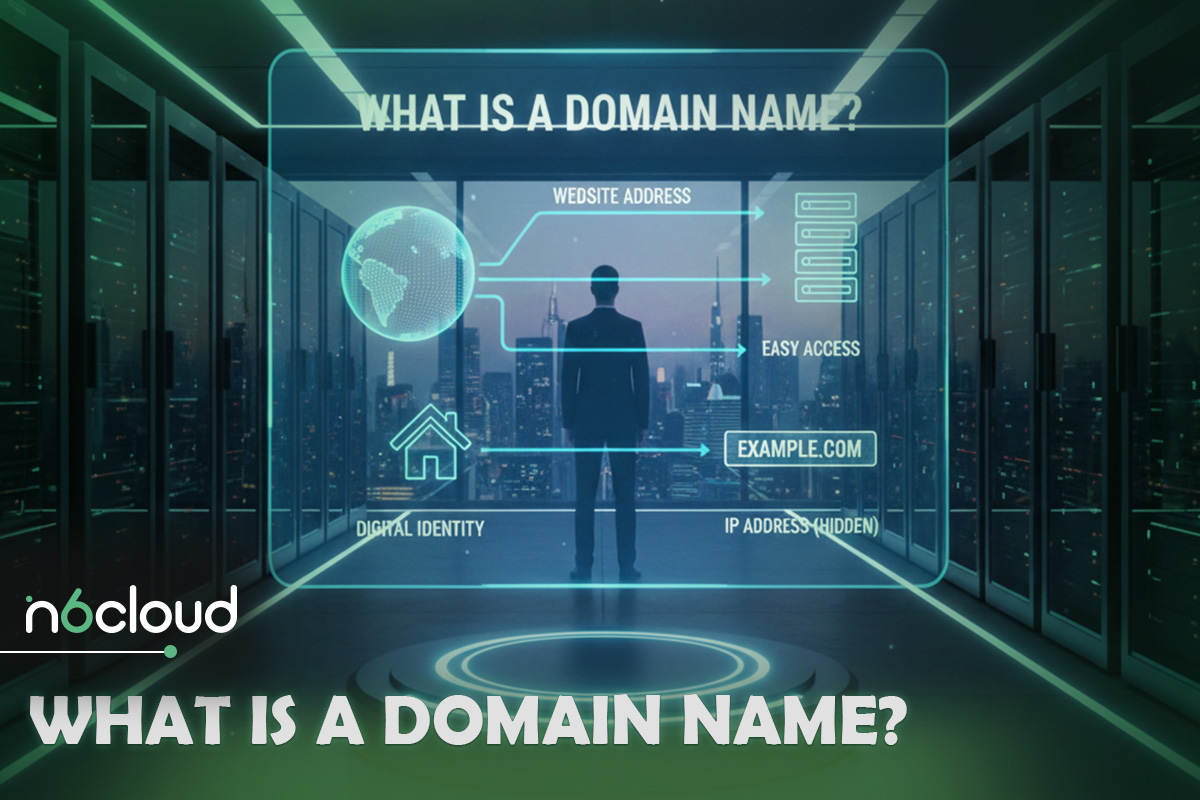
A domain name is the web address that people type into their browser to visit your website. It is the readable and memorable name that represents your brand or business online. Instead of remembering a long string of numbers, users rely on domain names to access websites quickly and easily.
Behind the scenes, the internet does not actually understand names. Every website lives on a server identified by a numerical IP address, such as 192.0.2.1. These numbers are how computers communicate with each other, but they are not practical for humans to remember. The domain name acts as a friendly label that points to the correct IP address, allowing browsers to find the server where your website is hosted.
From a branding perspective, your domain name plays a major role in how your business is perceived. A clear and professional domain builds trust, improves memorability, and makes it easier for customers to return to your site. Choosing the right domain name is not only a technical step, but also an important marketing decision.
Understanding Domain Name Structure
Every domain name is made up of two main parts that work together. The first part is the second level domain, which is usually the name of your business or brand. This is the most recognisable portion of the domain and the part users associate directly with your website identity.
The second part is the top level domain, often referred to as the extension. This appears after the dot and helps provide context about the website. Some extensions are intended for general use, while others are tied to specific countries or purposes. Together, these two components form a complete domain name that can be registered and used on the internet.
Common Types of Domain Extensions
There are many types of domain extensions available today, but they generally fall into two main categories. Generic top level domains include widely recognised extensions such as .com, .org, and .net. These are commonly used by businesses, organisations, and personal websites around the world and are often seen as the default choice for global audiences.
Country code top level domains are tied to specific countries or regions, such as .ca for Canada, .us for the United States, or .uk for the United Kingdom. These extensions are often used by businesses that want to emphasise a local presence or target a specific geographic market. For Canadian businesses, using a .ca domain can help reinforce trust and local relevance with domestic customers.
What Is Web Hosting?
While a domain name helps people locate your website, web hosting is what makes your website actually accessible online. Web hosting is a service that provides space on a server where your website files, images, databases, and applications are stored. When someone visits your domain, these files are delivered from the server to their browser.
Web hosting providers are responsible for maintaining the physical and virtual infrastructure that keeps websites running smoothly. This includes ensuring servers remain online, protecting them from security threats, managing network connectivity, and offering technical support when issues arise. Reliable hosting is essential for website speed, uptime, and overall user experience.
For beginners, it is important to understand that not all hosting services are the same. Different types of hosting exist to support different levels of traffic, performance requirements, and technical control. Choosing the right hosting solution depends on the size of your website, your growth plans, and how much management you want to handle yourself.
Types of Web Hosting Solutions
Shared hosting is often the starting point for new websites. In this setup, multiple websites share resources on the same server, which helps keep costs low. It is suitable for small sites, blogs, and early stage business websites that do not yet receive heavy traffic.
Virtual private server hosting, commonly known as VPS hosting, offers a more advanced option. Although multiple websites still exist on the same physical server, each site is allocated its own dedicated portion of resources. This provides better performance, increased control, and greater stability compared to shared hosting.
Cloud hosting takes a different approach by using a network of interconnected servers rather than relying on a single machine. This structure improves reliability and scalability, allowing websites to handle traffic spikes more effectively. Cloud hosting is often chosen by growing businesses that need flexibility and consistent performance.
Dedicated hosting is the most powerful option available. In this case, an entire physical server is reserved for one website or organisation. This provides maximum performance, full control over server configuration, and the ability to handle very high traffic volumes. Dedicated hosting is typically used by large businesses or websites with specialised requirements.
How Domain Names and Web Hosting Work Together
Understanding how domain names and web hosting interact behind the scenes can remove much of the mystery around how websites actually load on the internet. Although this process happens in seconds, several technical steps occur every time someone visits your site.
When a user types your domain name into a browser, the browser does not immediately know where your website lives. Instead, it asks a global network of servers known as the Domain Name System, or DNS, for help. DNS acts like a massive directory that matches domain names to their corresponding IP addresses. Once the correct IP address is found, the browser knows which server it needs to contact.
After the IP address is resolved, the browser sends a request to the server provided by your web hosting service. This server stores all of your website’s files, including text, images, styles, and databases. The server then responds by sending those files back to the visitor’s browser, which assembles them into the website that appears on the screen.
This entire process depends on both components functioning correctly. If your domain name is not properly connected to your hosting server, visitors will not reach your website. If your hosting server is offline or misconfigured, the domain name will still exist, but it will lead to errors instead of a working site. This is why domain names and hosting must be correctly linked and maintained together.
Should You Buy Domain and Hosting Together or Separately?
One of the most common questions beginners ask is whether it is better to purchase a domain name and web hosting from the same provider or keep them separate. There is no single correct answer, but understanding the advantages of each option helps you make a confident decision.
Buying both services together is often the easiest path for first time website owners. Many hosting companies simplify the setup process by automatically connecting the domain to the hosting account. Billing is also consolidated, which reduces administrative effort. In some cases, providers offer a free domain for the first year when hosting is purchased, which can lower initial costs.
Buying domain and hosting separately offers more flexibility and control. Your domain name remains independent of your hosting provider, which makes it easier to switch hosts if your needs change. Some businesses prefer this approach for added security and long term stability, especially as their website grows in importance.
From a performance and reliability perspective, the most critical decision is the quality of the hosting service itself. Your website speed, uptime, and visitor experience depend heavily on the infrastructure behind it. Choosing a reliable Web Hosting provider ensures that once visitors reach your domain, they experience a fast and stable website that reflects positively on your business.
Final Thoughts: You Need Both to Build a Real Website
Launching a website becomes much less intimidating once the difference between a domain name and web hosting is clear. A domain name gives your website an identity and makes it accessible to the world. Web hosting provides the foundation that supports your content, performance, and growth.
If the internet were a digital city, your domain would be the address that appears on the map, while web hosting would be the building standing at that location. An address without a building leads nowhere, and a building without an address remains unseen. A successful website depends on both working together seamlessly.
By understanding these fundamentals before launching your site, you set yourself up for smoother setup, fewer technical issues, and better long term results. Whether you are building a personal project or starting a business, making informed choices at this stage saves time, money, and frustration down the road.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, you can purchase a domain name on its own without immediately setting up web hosting. This is common when someone wants to secure a business name or reserve a domain for future use. In this situation, the domain will not display a website until it is connected to a hosting service, but ownership of the name is protected as long as it is renewed on time.
Yes, changing your web hosting provider does not require changing your domain name. When you move to a new host, you simply update your domain’s DNS settings so that it points to the new server. Visitors will continue using the same domain, but the website content will be delivered from the new hosting provider.
No, domain names are not owned permanently. They are registered for a fixed period, usually between one and ten years. To keep the domain, you must renew it before it expires. If a domain is not renewed, it may become available for others to register, which can be a serious risk for businesses.
Technically, yes, a website can be accessed using an IP address instead of a domain name. However, this approach is strongly discouraged. IP addresses are difficult to remember, look unprofessional, and can negatively impact credibility, branding, and search engine visibility. A domain name is essential for any serious website.
Yes, a functional website requires both. The domain name allows people to find your website, while web hosting stores and delivers the website content. Without hosting, the domain leads nowhere, and without a domain, the website becomes difficult for users to access and trust.
Yes, many hosting plans allow you to host multiple websites under a single account. Each domain can be connected to its own website files within the hosting environment. This is a common setup for entrepreneurs or businesses managing several projects or brands.
No, the type of hosting you choose does not change your domain name itself. However, hosting quality directly affects how your website performs once visitors reach your domain. Faster servers, better uptime, and stronger security all contribute to a better experience for users accessing your site.